Main Course 1-1 / PREPOSITIONS / Day 1 of 2
GENERAL AIMS
- To introduce what prepositions are and how they’re used
- To demonstrate that deciding which preposition to use can be based on understanding the meaning of the preposition, or through collocation
STEP SUMMARY
|
A |
Introduction |
What are prepositions? |
|
|
B |
Logical meanings |
Learning meanings of prepositions |
|
|
C |
Collocation |
Typical groupings |
|
RECOMMENDED LEVELS
Intermediate Up
ACTIVITY TIME
15-20 minutes
MATERIALS
Handouts for students:
HO1 pyramid & collocation worksheet
SPECIAL NOTES
– Note 1
– Note 2
Quickpage
Class Plan
PART A: TITLE
|
A |
1 STEP |
INTRODUCTION WITH HANDOUT PREPOSITIONS |
|
|
a) |
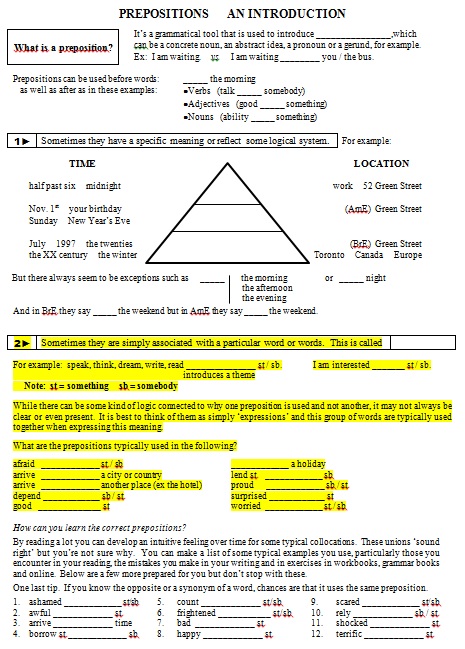
Give the students HO1 (Handout #1) and go over the introduction (until the first flag marker) together, eliciting the words to fill in the blanks as you go along. |
||
PART B: PREPOSITIONS MAKING SENSE
(HAVING LOGICAL MEANINGS)
|
B |
STEP 1 |
LOGICAL MEANINGS INTRODUCTION PREPOSITIONS |
|
|
a) |
Have the students look at the pyramid with the examples of time and location. |
||
|
b) |
Point out that the bigger portion of the pyramid reflects a big quantity of time (ex: months, years) or a big physical area (ex: cities, countries). |
||
|
c) |
Point out that the top part shows a smaller, more precise point in time or space such as the exact time or location. |
||
|
d) |
Point out the middle section is a more intermediate interpretation with the specific preposition introducing days (in different possible ways) or, in American English (AmE), the name of the street. In British English (BrE) a street can be interpreted as a sufficiently big area to be included in the larger bottom group. |
||
|
B |
STEP 2 |
LOGICAL MEANINGS FILLING IN THE PYRAMID PREPOSITIONS |
|
|
a) |
Elicit the 3 prepositions needed to complete the pyramid and have the students write them in the corresponding places on their handout. |
||
|
b) |
Remind them this pyramid serves more as a guideline than as an absolute rule. However, it can still be very useful if one is not sure which preposition is appropiate. Making an educated guess using this guideline will increase their chances of choosing the right preposition. |
||
|
B |
STEP 3 |
LOGICAL MEANINGS THE EXCEPTIONS PREPOSITIONS |
|
|
a) |
Do the remaining 4 gap-fills together as a class. |
||
PART C: COLLOCATION
|
C |
STEP 1 |
COLLOCATION INTRODUCTION PREPOSITIONS |
|
|
a) |
Fill in the box at the end of the Part 2 heading: Ask the students for the word which refers to the situation where words are typically grouped together. Example: small, medium & large shirts (in a shop) not small, medium & big ANSWER: collocation |
||
|
b) |
Ask them for the prepostition which typically introduces a theme (following any of the verbs given) ANSWER: about |
||
|
c) |
Is it the same preposition used when following interested ? ANSWER: no |
||
|
d) |
Elicit the appropiate preposition. ANSWER: in |
||
|
e) |
Ask the students why about is not correct. ANSWER: because in collocates with interested |
||
|
C |
STEP 2 |
COLLOCATION GAP-FILL PREPOSITIONS |
|
|
a) |
Have the students individually attempt to fill in the gaps for the words afraid to worried. |
||
|
b) |
Students compare their answers in pairs or groups of three. |
||
|
c) |
Go over the answers together, pointing out that these prepositions typically collocate with those words |
||
|
C |
STEP 3 |
COLLOCATION REVIEW PREPOSITIONS |
|
|
a) |
Have the students turn over their papers. |
||
|
b) |
Elicit the prepositions either from the class as a whole or soliciting directly from different students. “Jordi, afraid _____ something or somebody. What’s the preposition?” |
||
|
c) |
Point out that in many cases, it’s simply remembering what that particular group of words is, functioning as a set expression. |
||
|
d) |
Place the students into pairs and have them taking turns asking their partner questions as modelled in step b. Then they change roles. Note: The ‘teacher’can refer to the handout, but the ‘student’ cannot. |
||
|
C |
STEP 4 |
COLLOCATION HOMEWORK PREPOSITIONS |
|
|
a) |
Read to the students or have them read the paragraph at the end of HO1 following “How can you learn the correct prepositions?” as well as the final tip. |
||
|
b) |
Assign numbers 1 – 12 for homework. |
||